About our group
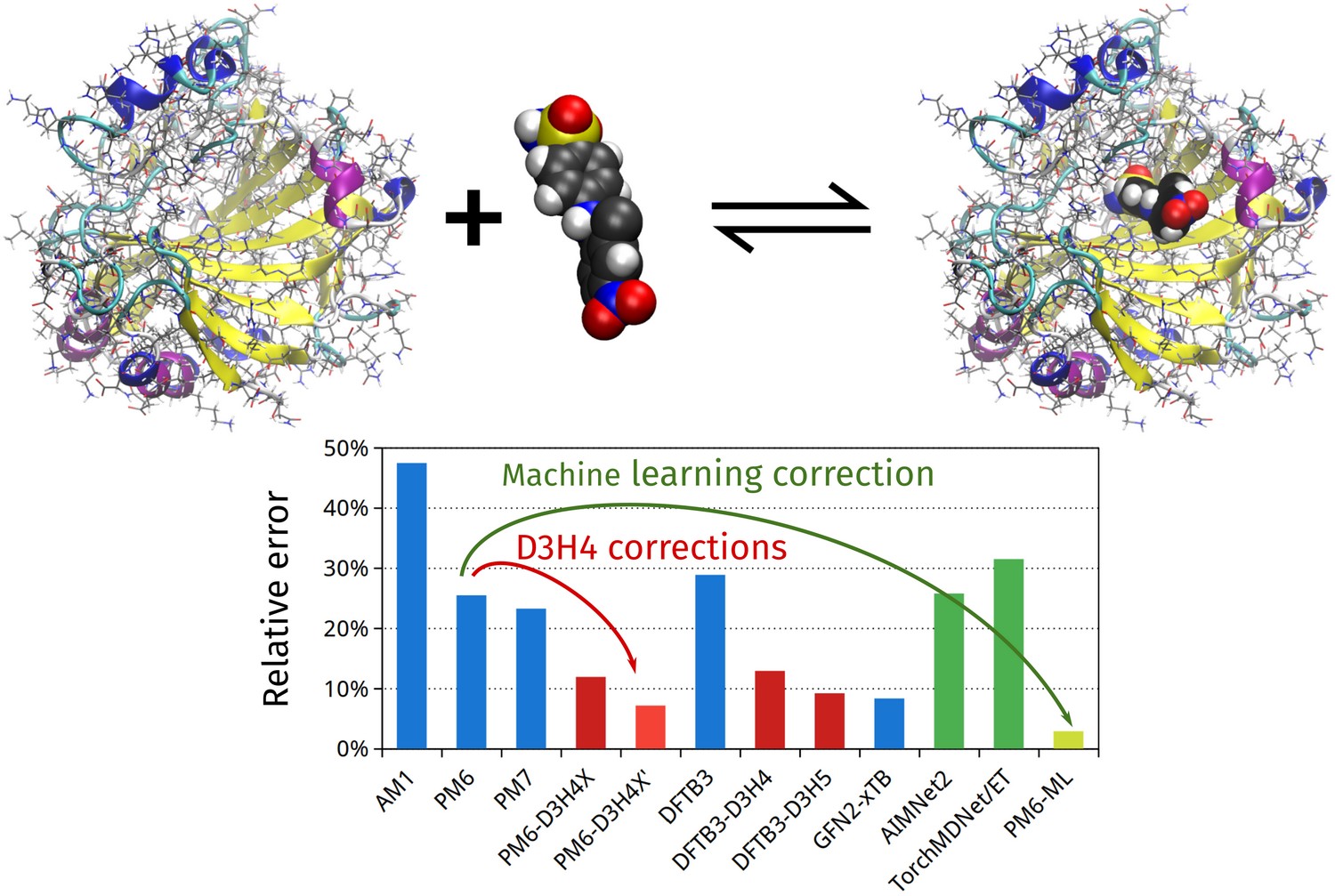
We develop efficient computational chemistry methods and apply them to the study of biomolecules. By combining semiempirical quantum chemical calculations and machine learning techniques, we are able to compute large systems containing thousands of atoms with unprecedented accuracy. This work is also supported by accurate benchmark calculations and the study of the fundamental mechanisms of non-covalent interactions.
We focus on the calculation of the binding affinity of protein-ligand complexes, a quantity crucial for computer-aided drug design. Our methodology combines the unique advantages and accuracy of quantum mechanical calculations with the efficiency required for applications to real-world problems.
The group collaborates with biochemists and medicinal chemists at IOCB as well as with leading pharmaceutical companies on practical applications of our methodology.
Publications